Lajos Kossuth: a Hungarian Hero Celebrated in America
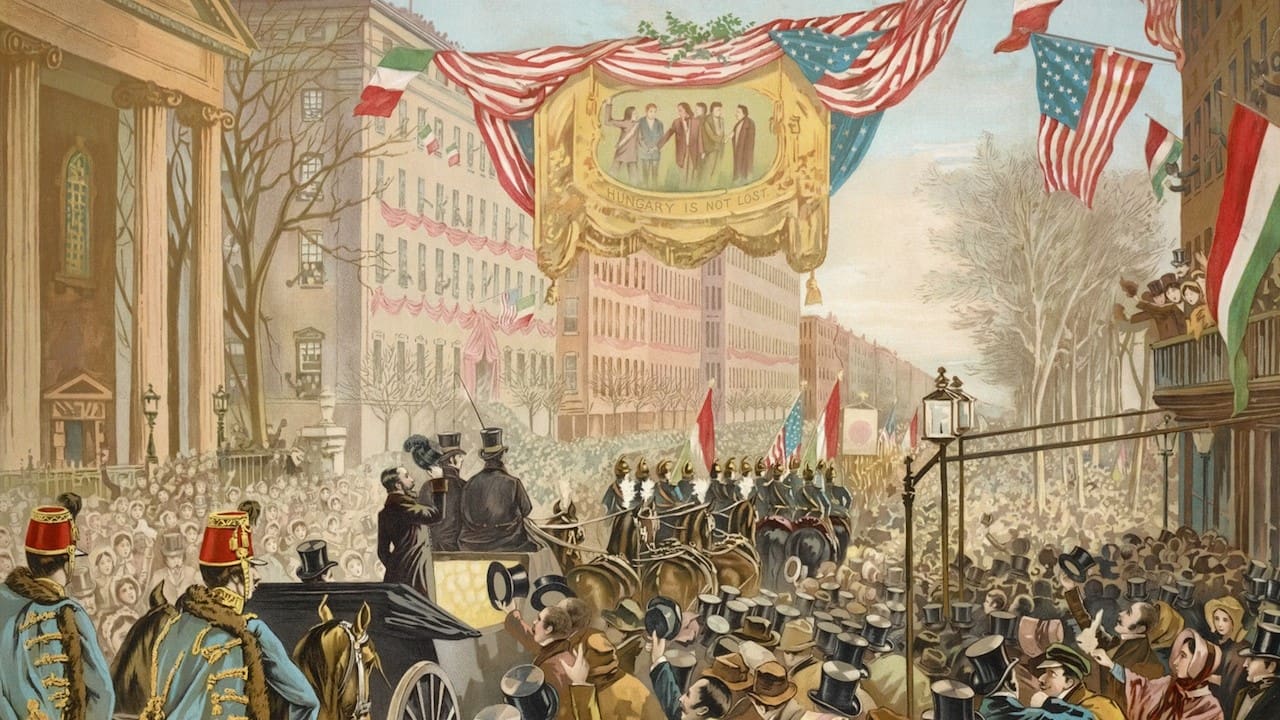
Renowned Hungarian revolutionary and statesman Lajos Kossuth arrived on the shores of the United States on 6 December 1851. He was received by a warm welcome and outpour of enthusiasm, from the highest ranking politicians and the ‘common folk’ alike, who lauded him for his pursuit of Hungarian freedom.