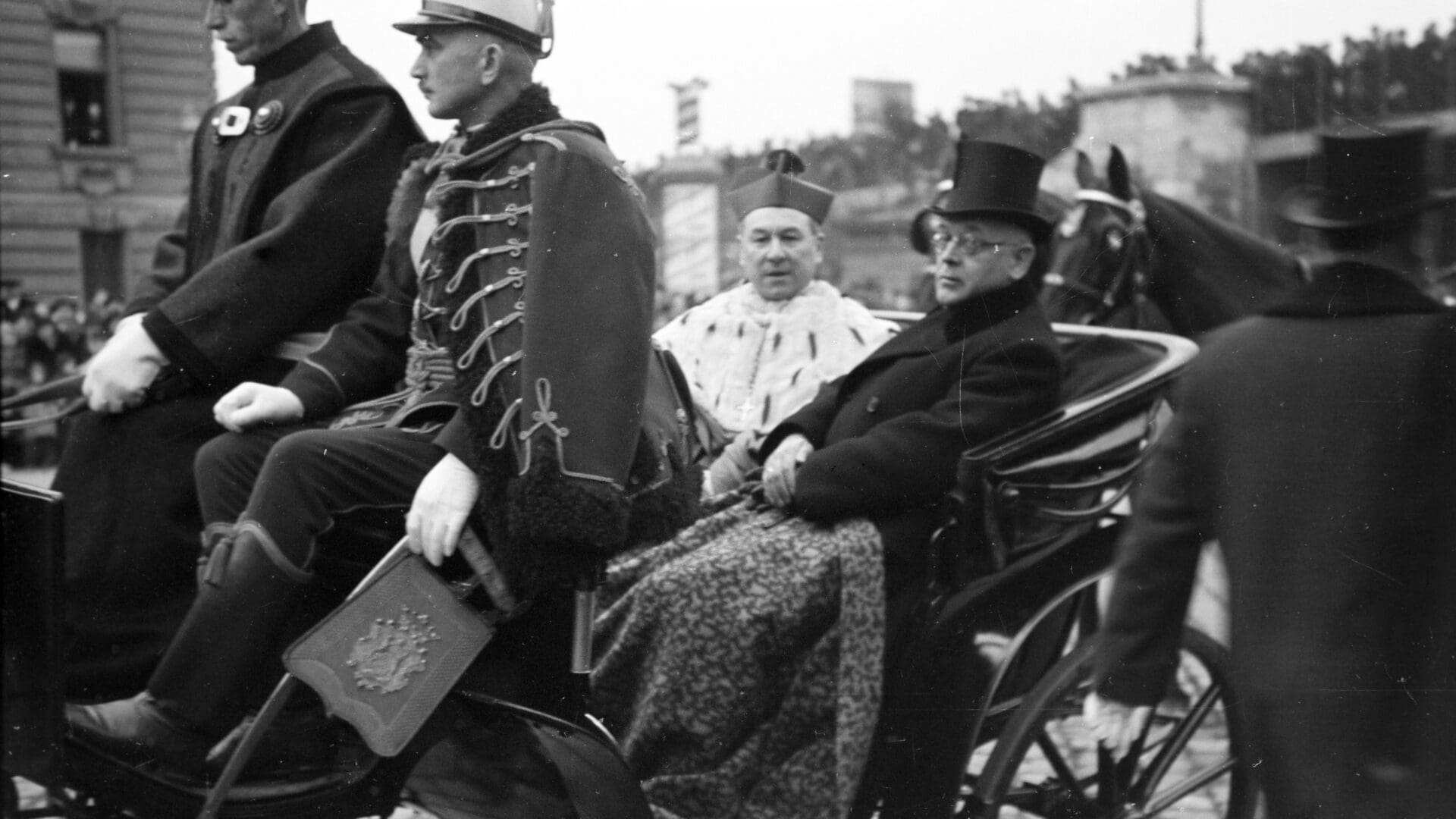
The French Revolution, the Napoleonic wars, the emergence of capitalism, and the development of the first nation-states put both Protestant and Catholic churches in a position they could never have dreamed of a few decades before. Even though reconciliation between state and church came fast, these events served as a Rubicon in Western history and civilization. The clergy, regardless of its faith, had to rediscover itself in a totally different political and socio-cultural environment. The insightful book Theologians on Modern Politics, presented on 4 June, attempts to demonstrate the changing nature of both religious institutions and the faith itself, which allowed Christian ideas and communities to remain key players in modern politics.