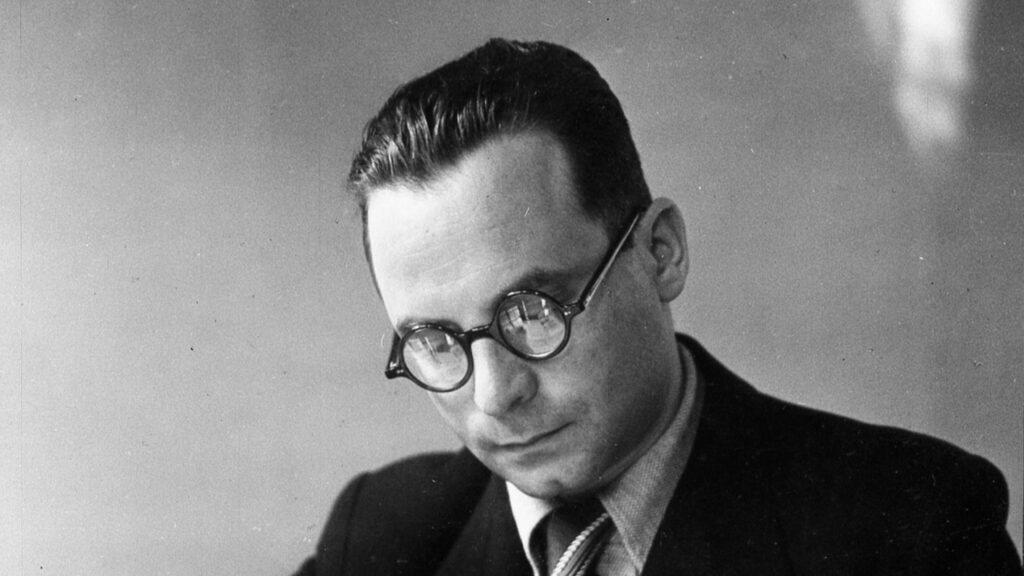





Was the great writer Antal Szerb beaten to death by a fellow Jew, as a postwar indictment and online claims suggest? Drawing on court records, testimonies, and archival evidence, this piece revisits a murky People’s Court case to separate hearsay, vengeance, and historical fact.

‘These cases highlight the cruel paradox of 1951: people who had already suffered persecution were once again uprooted by a regime that judged them by social labels rather than personal history.’
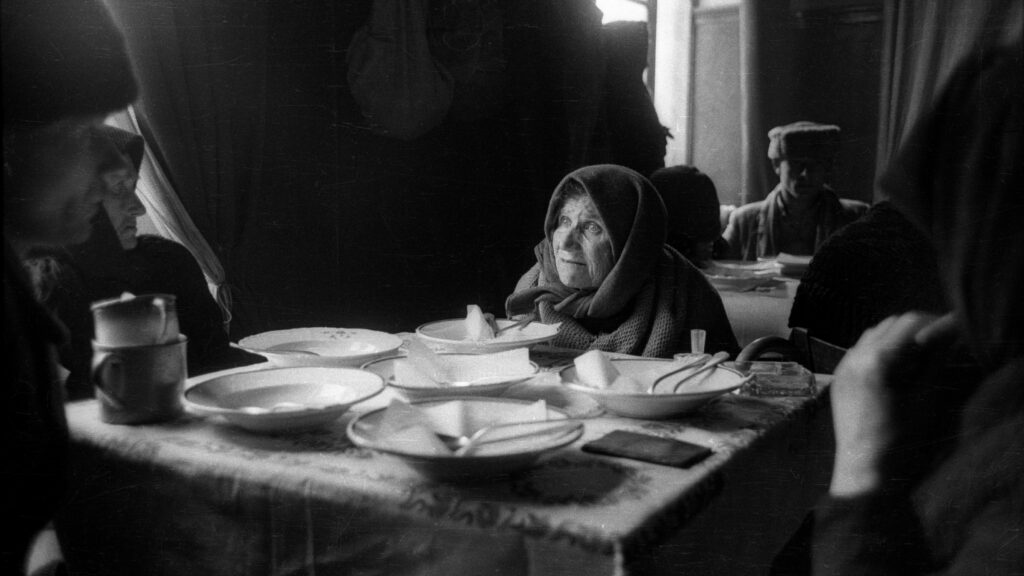

‘Elderly, much like children, often need the power of the state for protection, but in this case, it was the state itself which saw them as “class enemies”. These old Hungarian citizens, whatever their political beliefs were, had trouble taking care of themselves, yet the Communist state…branded them enemies of the people and forcibly removed them from their homes…’
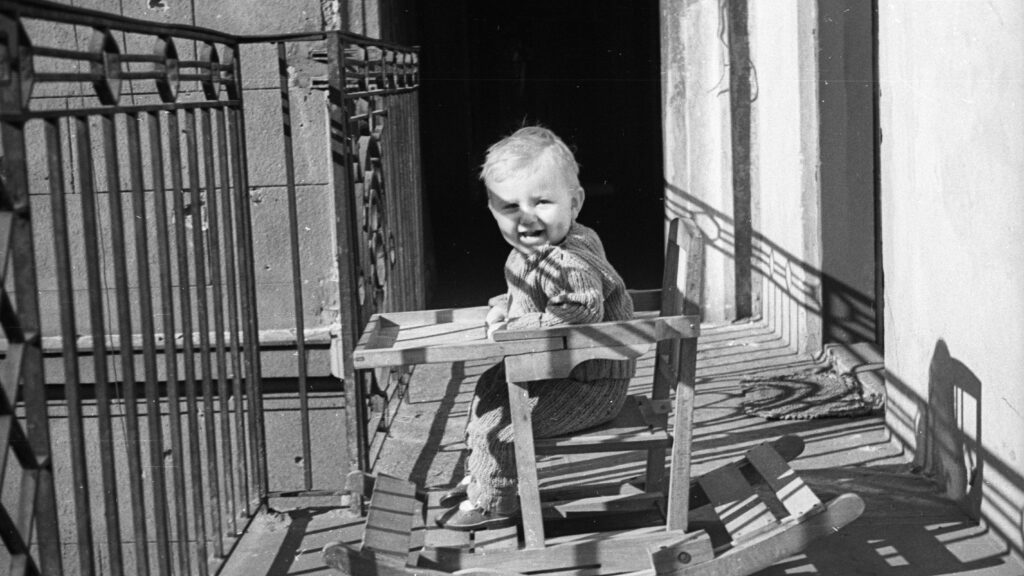

‘Some were permitted to take shelter with relatives in the countryside, but the majority of such requests were rejected. Only in the rarest cases did deportees arrive under relatively consolidated conditions…This article will focus especially on deported families with little children, and our further articles will inspect other interesting cases as well.’

‘From 1974 to the late 1980s, Hungary’s state security closely monitored the Turkish embassy at 45 Úri Street in the Buda Castle, keeping tabs on diplomats, their residences, and even personal correspondence. Newly examined documents reveal how counterintelligence observed NATO diplomats, highlighting both the meticulous methods of the secret services and the routine nature of embassy life.’
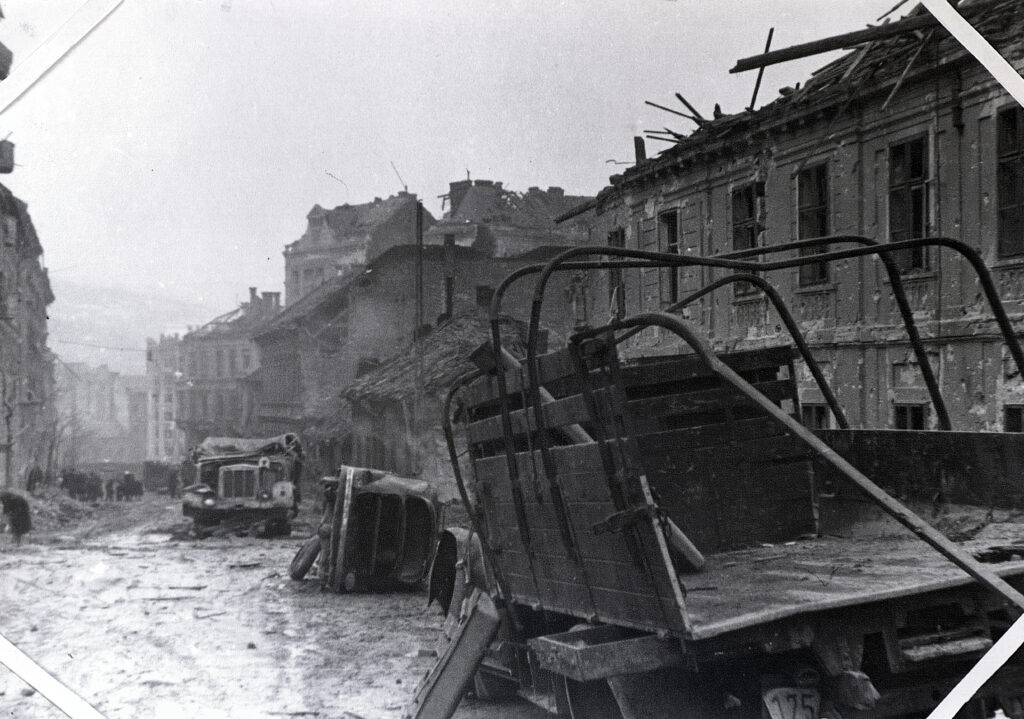

‘On Christmas day in 1944 Hungary, illusion and reality collided. The promise of “liberation” or “redemption” was drowned out by violence, coercion, and fear on all sides. What survives of that Christmas are the testimonies, the fragmentary voices that reveal how ordinary lives were crushed between two brutal systems at the very moment meant for peace.’
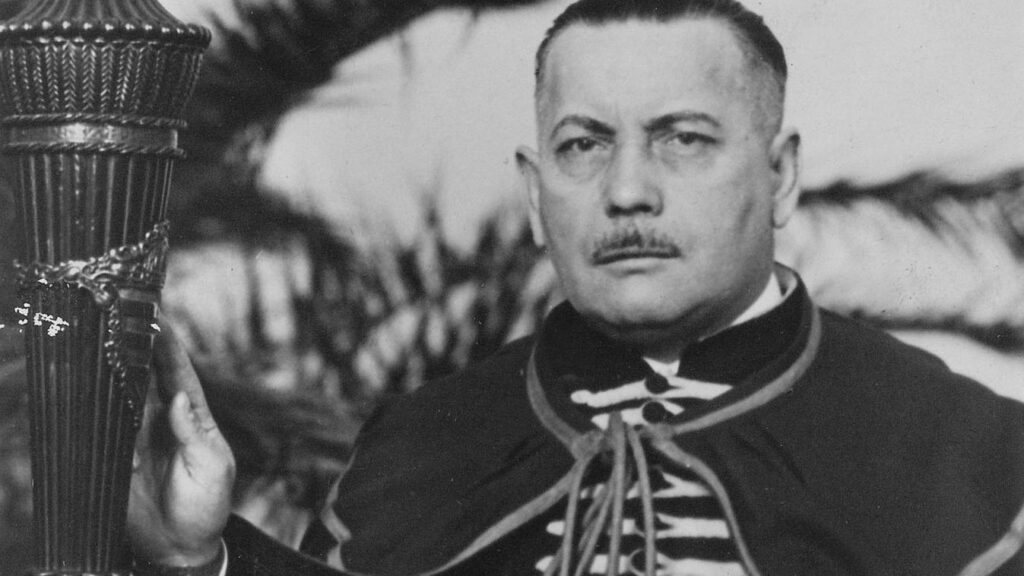

‘It is a fact that if there are enigmatic figures in 20th-century Hungarian history, Kálmán Rátz is certainly among them.’
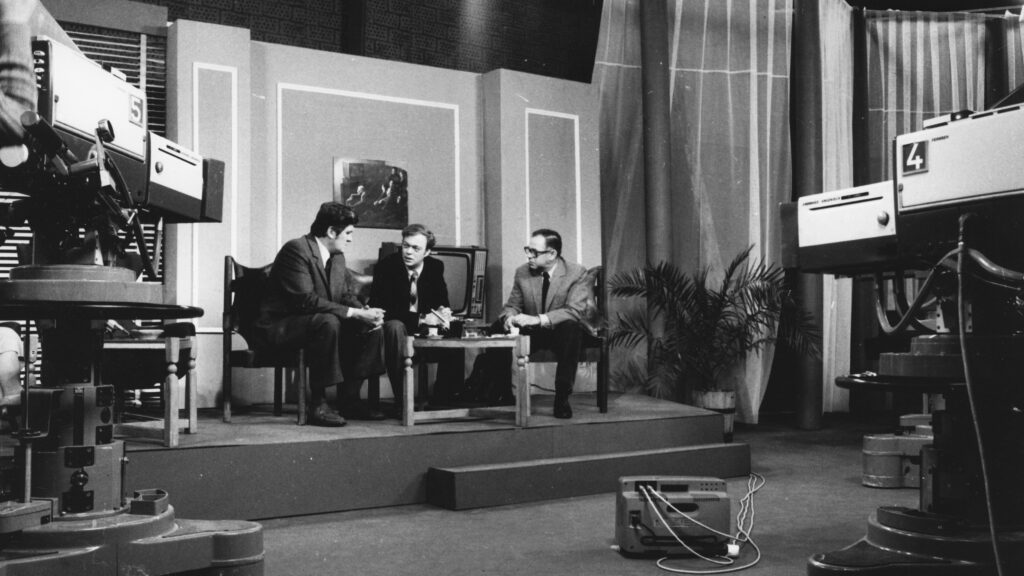

‘From the above, it is clear that “Filmes” was the “social contact” of the Hungarian intelligence service who attended Münch’s reception and who was also the director of the TV series Századunk—a description that fits only one person, namely Péter Bokor.’
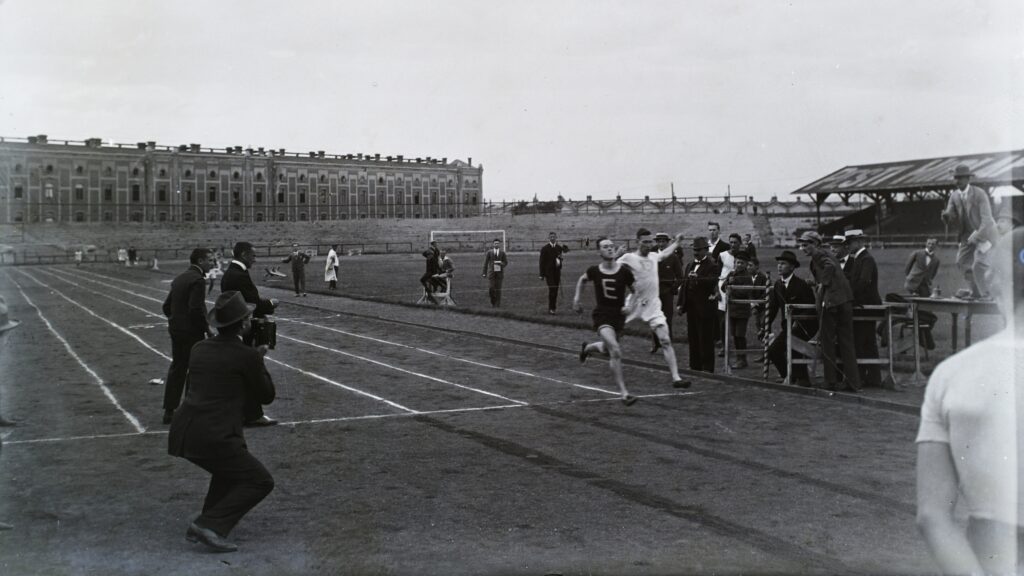

‘The White Terror was largely a series of events in the countryside, and although atrocities and murders did occur in Budapest as well, these were not characteristic of the 1st District. Nevertheless, at least one murder is known to have taken place in the 1st District, specifically in the Nándor Barracks on Kapisztrán Square…’
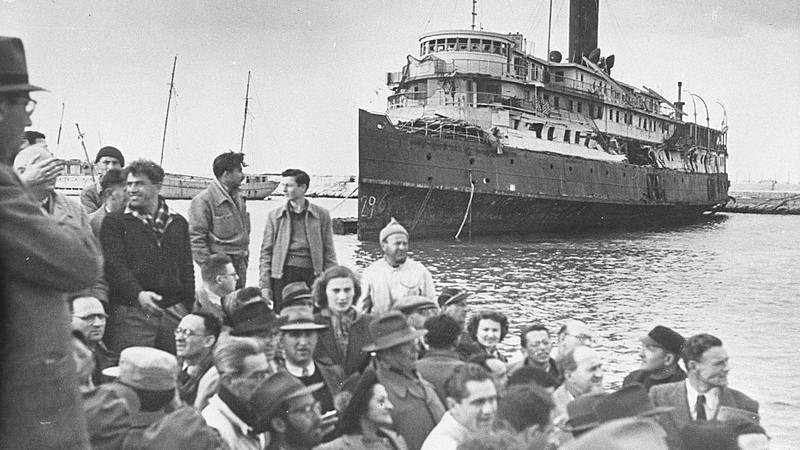

‘In shedding light on his work and the history of the Hungarian Betar movement, we not only recover a lost voice of right-wing Zionism but also gain a fuller, more nuanced understanding of Jewish history in Hungary before, during, and after the Holocaust.’
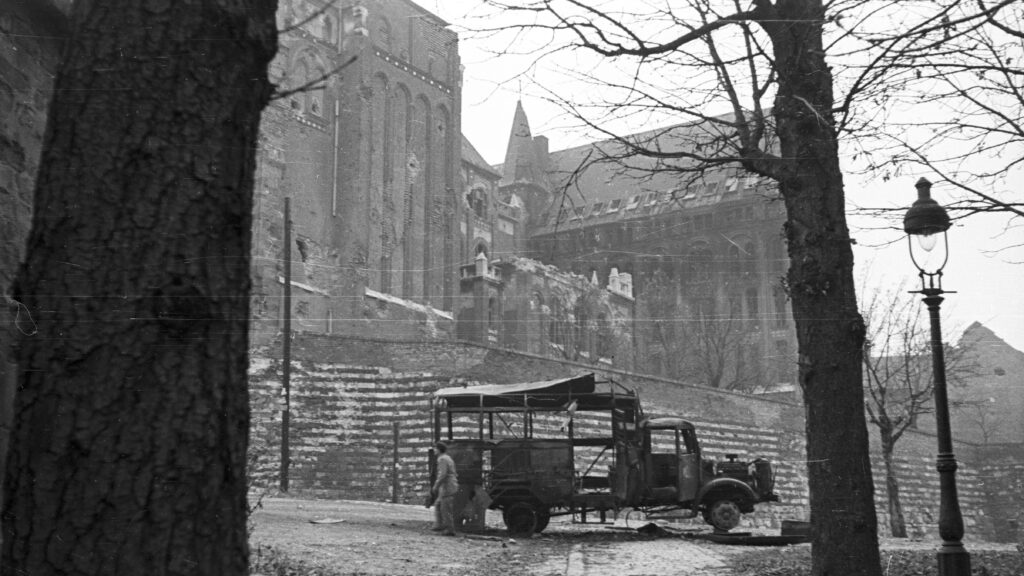

‘During the fighting, two primary schools, one high school, and one kindergarten in the district were damaged, with total costs amounting to 150,000 forints; 20,000 of this was for the physics laboratory at Szilágyi High School alone.’
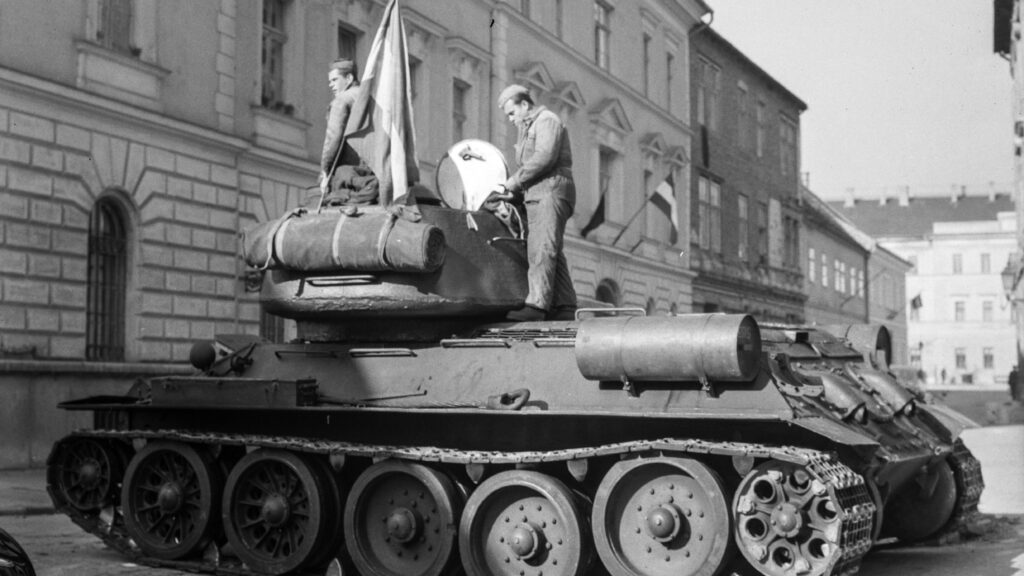

‘Here, we will mostly focus on Batthyány’s role as one of the rebel leaders mentioned; his trial papers have survived to the greatest extent. In October 1959, an investigation was launched “in connection with the crimes of the counter-revolutionaries of Széna Square”, and “during this investigation, we identified several individuals who had not yet been held accountable…”’

‘The events in District I during the Hungarian Soviet Republic give a very good account of how fear, miscommunication, and ideological zeal combined to ignite violence and unrest…From armed requisitions to fatal clashes over religious processions, the communist Council Republic’s heavy-handed responses reveal the fragility of order under a revolutionary dictatorship.’
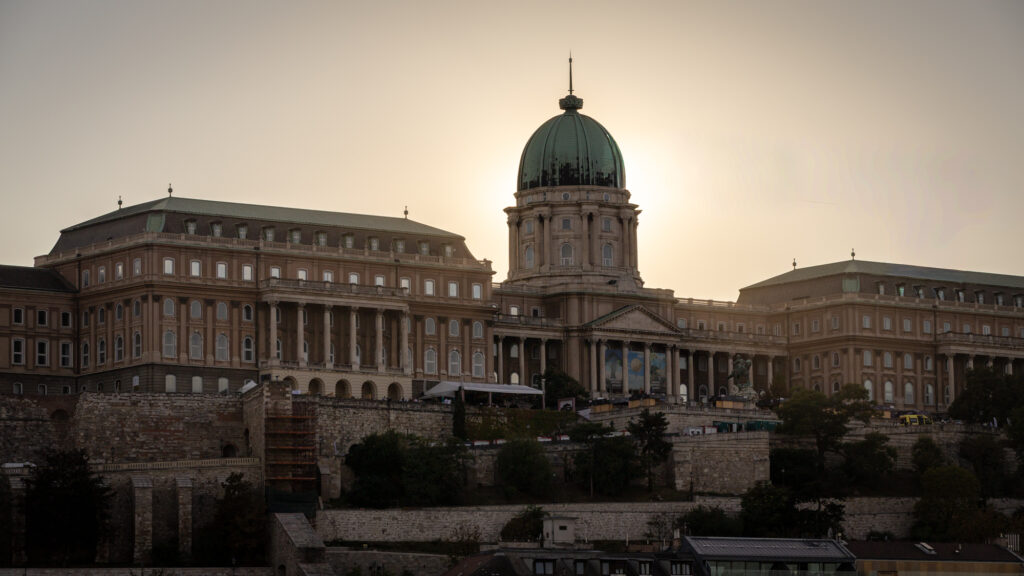

‘Despite its grandiose displays and ideological fervour, the Council Republic’s efforts in Buda Castle exposed the fragility and contradictions of revolutionary rule. Eventually, the events reveal how the conflict between radical ideals and human behaviour shaped both the promise and the pitfalls of early Hungarian communism.’
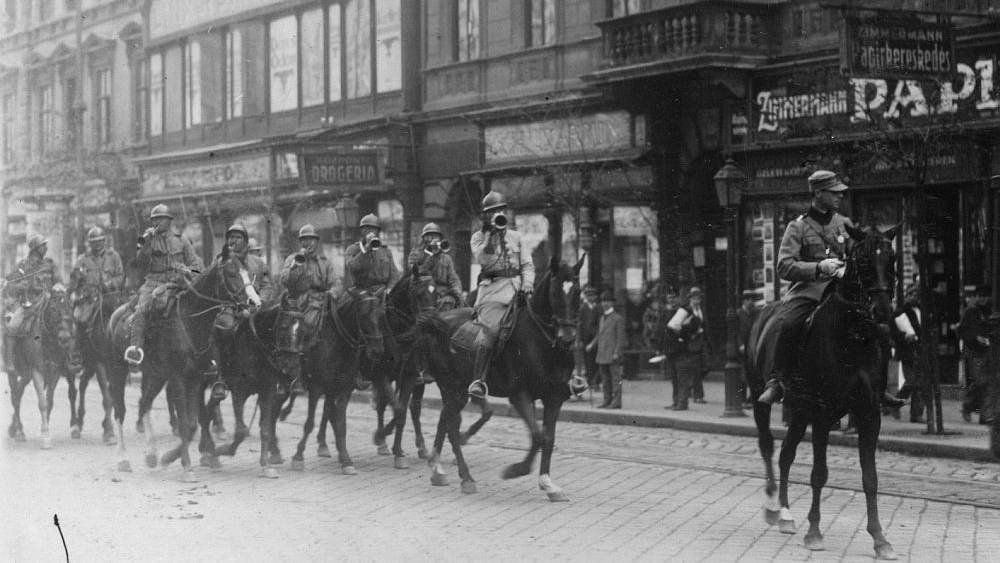

‘In the name of both myself and all the residents of the house, I lodge this complaint against unknown Romanian soldiers who, after becoming intoxicated day after day in the tavern located on the ground floor of the building, come out into the courtyard and recklessly fire their weapons with live ammunition, constantly endangering the bodily integrity and lives of the residents.’
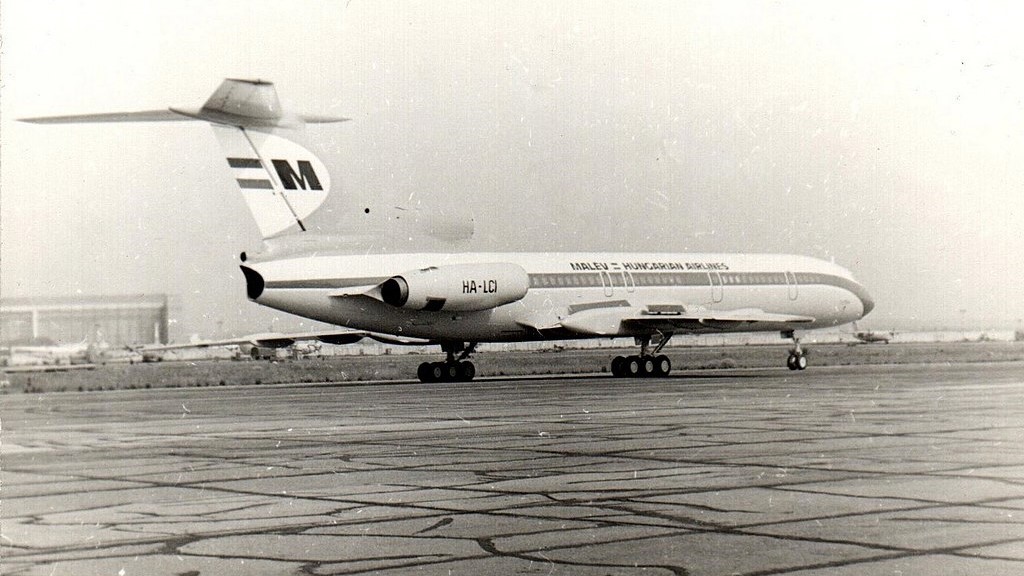

‘According to the cable, the Hungarian–Soviet investigative team was surprised that the Lebanese government had not conducted autopsies on the bodies “to determine whether the plane exploded before the crash”. Finally, the cable cites the French-language press in questioning how it was possible that only the conversation involving this aircraft failed to be recorded.’

‘Ultimately, the story of the “big tree gang” illustrates how social anxieties, political agendas, and propaganda intersected in late-1960s Hungary. The files, reports, and novels documenting their lives offer a fascinating glimpse into a vanished world where surveillance and Marxist ideology shaped even the smallest acts of everyday life.’

‘Residents, businesses, and even foreign visitors were catalogued, assessed, and placed under surveillance based on their perceived political reliability. This extensive, decades-long system reflects the regime’s pervasive fear of dissent and its determination to control both people and urban spaces.’

‘“The person of Zoltán Liska, chaplain serving at the Castle parish, has for some time been of interest to the state security organs…The wording of his speeches violates the agreement between church and state.” It is beyond doubt that the priest’s messages sometimes encouraged his faithful toward active, courageous ways of keeping strong Christianity forced underground.’
‘Tóth informed the choir members that he had “received an ultimatum from the Ministry of the Interior”, which caused great outrage—someone reportedly shouted: “This can’t happen in 1966 Hungary!” But it did happen.’

In 1982, Hungary’s state security services launched Operation ‘Crystal’ to surveil an IMF delegation staying at Budapest’s Hilton Hotel. Phones were tapped, documents copied, and economic secrets uncovered—all under the watchful eye of the Kádár regime. The operation reveals the extent of Cold War-era espionage woven into everyday locations.

‘Whether, in light of all this, she truly managed—as she claimed in her oral history interview—“to strictly observe Jewish teachings” is something only posterity can judge.’

Although Géza Seifert later became a loyal Communist collaborator and President of the National Representation of Hungarian Israelites, he briefly led a ‘revolutionary committee’ within the Budapest Jewish community during the 1956 uprising—a role long forgotten and absent from scholarly accounts. This article revisits that moment, based on newly examined archival sources.

‘I’m a Jew who does not bow down and does not beg to be heard, but states his opinion without hesitation.’
‘At one point, Benedek remarked that “the communists…have committed many crimes and have a lot of blood on their hands,” just like the Catholic Church—but, he added, at least the Catholics are Christians.’

In the early 1950s, Hungary’s secret police targeted the Bécsi Kapu Square Lutheran congregation in one of its most extensive church surveillance operations. Despite amateur methods and critical errors, including mistaken identity, the investigation dragged on—highlighting both the paranoia and inefficiency of Rákosi-era state security.

A new volume by historian István Pál explores Hungary’s Cold War espionage operations in the US and UK. New York–Washington–London reveals key cases from 1950–1970, offering rare insight into the shadowy world of state socialist intelligence and its often flawed, yet revealing, tactics abroad.
‘Overall, it is clear that Kraus was a religious Israeli Hungarian publicist who rightly earned the communist dictatorship’s ire. To hinder his activities, a covert procedure was launched, and his conversations and correspondence were monitored both directly and indirectly; in other words, he was treated as an enemy of the regime for decades.’

‘This does not ruin the research activities of “Lantos” in his civilian life, nor does it detract from his achievements as a historian. It merely points to the fact that even the most prominent public figures were sometimes “found” by state security, and some of them, for one reason or another, said yes to collaboration—even if the candidate was Jewish and the target was the State of Israel.’

‘The term “network” is somewhat misleading here, since these individuals were unaware of one another…The agents were connected to something, but not to each other—they were connected to state security, specifically through their handlers. The author describes this as an “extremely centralized, star-shaped network in which every element was linked to a single centre.”’