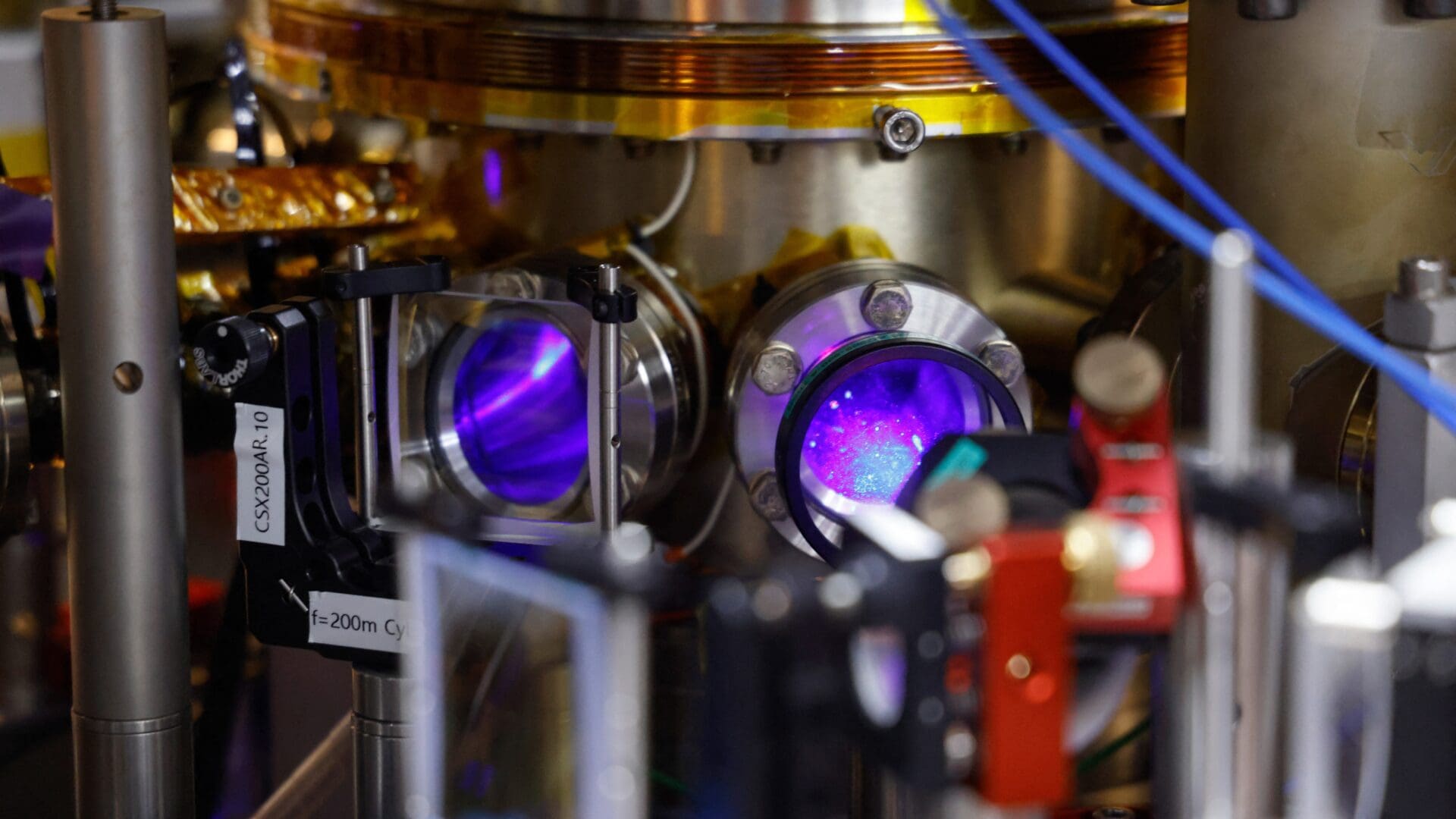
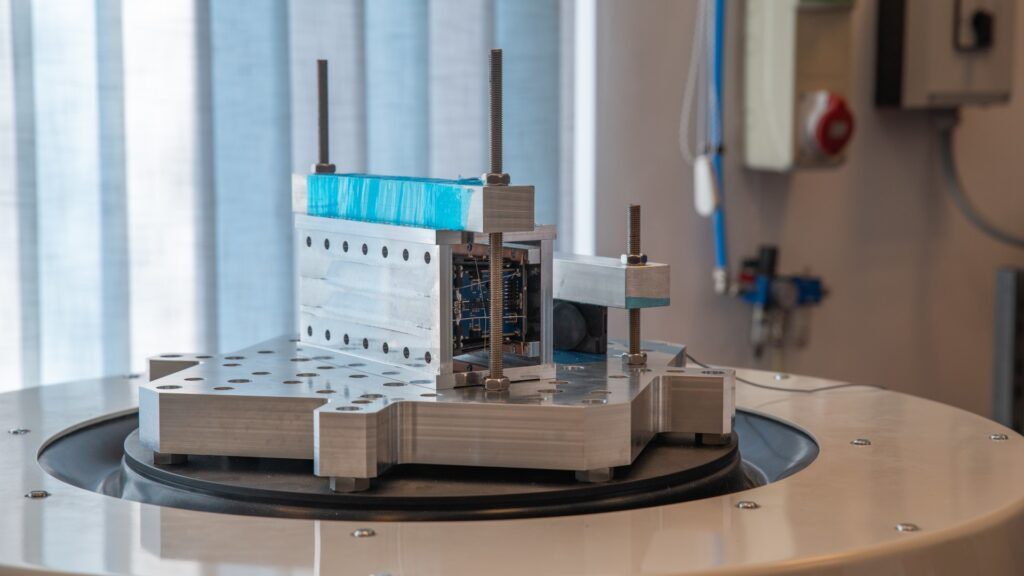
The specialists at the HUN-REN Wigner Research Centre for Physics are developing a next-generation quantum microscope within the framework of a recently initiated project, as announced by the institution on Monday.
Led by Ádám Gali, the research group is capable of measuring magnetic, electric, and mechanical fields, as well as temperature, with high spatial resolution, utilizing the unique properties of diamond nitrogen-vacancy centres. The aim is to create a tool that physicists, chemists, biologists, and engineers can use as a quantum sensor for the examination and qualification of various materials, providing unprecedented spatial resolution and sensitivity.
The project involves the design and implementation of special measurement methods for the quantum microscope, which, according to their knowledge, would introduce a unique device to the market, as no quantum sensor combining such components currently exists. Also, the measurement technique based on the unique nitrogen vacancy centre is considered a unique solution in Europe, and it is planned to be applied in the quantum microscope. The device’s unique selling point lies in its ability to operate at room temperature, not requiring special conditions, and consuming minimal energy.
Log into Facebook
Log into Facebook to start sharing and connecting with your friends, family, and people you know.
In its statement, the HUN-REN Wigner Research Centre recalls another project recently initiated under the leadership of Orsolya Kálmán and Zoltán Zimborás. The objective of this project is to integrate artificial intelligence in certain areas of quantum technology, developing a software package that applies machine learning and other artificial intelligence-based algorithms to make currently available, noisy quantum computers more efficient.
Primarily,
the project aims to develop an artificial intelligence-enhanced quantum gate translator
that incorporates a quantum error-reduction procedure. Additionally, as a test and potential industrial application, the project plans to devise quantum machine learning algorithms that can be amplified through the quantum hardware.
Both projects are set to continue until 2026 and are expected to significantly contribute to the work of scientific and industrial users in Hungary and Europe in the field of quantum technology, as stated in the release.
Related articles:
Sources: Hungarian Conservative/HUN-REN/MTI